It’s often claimed that good poker strategy involves a mixture of –
- Game theory
- Probability
- Psychology
- Statistics
In what precise ways do poker statistics contribute to a successful player's mindset?
Through poker statistics, players have the opportunity to modify their strategies and hone their skills.
In this piece, you will discover how to interpret and apply poker statistics through a variety of subjects covered below:
We will examine 7 different methods to apply statistics within the poker landscape.
1. Odds of Hitting a Hand
Poker players often make predictions regarding the probability of a specific hand making its mark; this estimation relies on the number of potential \" outs \" remaining in the deck.
For example, in Hold’em, a flopped flush draw The likelihood of hitting by the river is about 36%. Estimating these figures on the spot primarily falls under the study of probability rather than poker statistics.
When players endeavor to memorize key statistics in advance, this practice falls squarely into the domain of poker statistics.
Rather than calculating probabilities in the heat of the moment, seasoned players commit to memory the crucial statistics they need.
Below is an example of statistics that a poker enthusiast might strive to learn.
The table presented outlines the likelihood of completing various hands in Holdem , contingent upon the number of outs and the current stage of play.
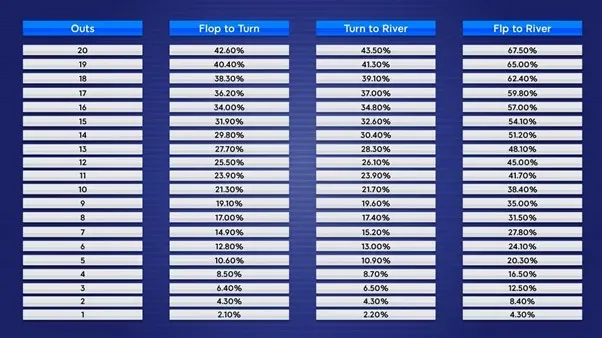 Chances Of Hitting Hands In Hold’em
Chances Of Hitting Hands In Hold’em
Naturally, all these statistics can be derived using methods from the field of probability.
However, trying to compute these figures mid-hand tends to squander precious time, prompting many players to prefer simply internalizing these vital statistics.
Chances of Completing a Hand – Essential Statistics
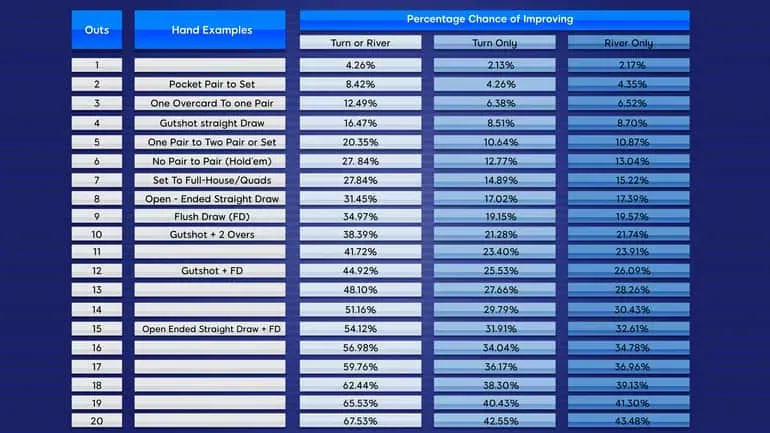 Hitting Specific Draws By The River
Hitting Specific Draws By The River
- Achieving a flopped flush draw by the river - 35% ",
' on the flop succeeds roughly 35% of the time by the river. Assuming we only see the turn, our chances of making the flush halve.',
"It's essential to keep in mind the statistics associated with realizing different types of hands. This approach is generally more effective than attempting calculations during the hand.
A flush draw Achieving a flopped open-ended straight draw by the river - 31.5%
) on the flop has approximately a 31.5% success rate by the river. As mentioned earlier, this presumes we will observe both the turn and the river. - Achieving a flopped gutshot by the river - 16.5%
An open-ended-straight-draw ( oesd A straight draw on the flop succeeds roughly 16.5% of the time by the river. - Flopping a set after entering with a pocket pair preflop - 11.8%
A gutshot Upon entering the hand with a pocket pair preflop, we will flop a set about
- 11.8% of the time. This statistic can assist in determining whether pursuing a set is a worthwhile strategy.
Both \"pot odds\" and \"break-even points\" can also be quickly calculated using probabilities. Yet again, numerous players prefer to memorize these essential statistics. set The above table might be perplexing for those lacking a background in poker theory .
2. Pot Odds and Break-Even Points
Equity Needed to Make a Call – Also called \"Pot odds\". These pot odds are distinct from the \"odds of hitting\" mentioned earlier regarding poker statistics.
When converted to a percentage, these numbers reveal the proportion of the total pot we would be wagering on a call.
Here is a quick explanation -
- This figure coincides with the necessary pot equity to achieve a break-even point when completing the action. Pot odds For instance, as indicated in the previous chart, if our opponent places a bet amounting to 50% of the pot, calling would entail investing 25% of the total pot.
If we are closing the action, we would require a minimum of 25% pot equity to break even .
– This statistic illustrates the bluff frequency required (at a given bet size) for a successful pot win to be directly advantageous (ignoring any pot equity).
For example, a bet of 50% of the pot must succeed 33.33% of the time for it to be viable. - Break-Even Point of Bluff While these calculations can be performed swiftly using probability, the majority of dedicated poker players lean towards a statistics-oriented strategy of simply memorizing all necessary values.
Pot Odds and Break-Even Points - Crucial Statistics
The subsequent table displays our pot odds (expressed as percentages) against standard bet sizes:
to call against a half pot bet on the river - 25%
When faced with a half-pot wager, we must have a winning likelihood of over 25% to call effectively. Remembering these foundational statistics is beneficial rather than trying to compute them during play.
| Facing Bet Size (%) | Pot Odds (%) |
|---|---|
| 20 | 14.29 |
| 25 | 16.67 |
| 33 | 19.88 |
| 40 | 22.22 |
| 50 | 25.00 |
| 60 | 27.27 |
| 66 | 28.45 |
| 70 | 29.17 |
| 75 | 30.00 |
| 80 | 30.77 |
| 100 | 33.33 |
| 150 | 37.50 |
| 200 | 40.00 |
- Required equity Required equity for a call when facing a pot-sized bet on the river - 33%
We must have a better hand more than 33% of the time to justify calling a pot-sized bet. We need not hold a favorable position to call since chips are already in play. - Break-even threshold on a half pot bluff on the river - 33%
A bluff at half pot becomes directly profitable if our opponent folds more than 33% of the time. It can be advantageous to bet with any two cards, particularly if we believe our opponent folds often. - Break-even threshold on a pot-sized bluff on the river - 50%
For a pot-sized bluff to yield profitability, it must succeed more than 50% of the time. - 3. Utilizing Poker Statistics for Database Analysis
Players in online poker generally monitor their hand history through poker tracking software, which records every hand played. This software compiles data to present critical poker statistics like the \"total number of hands played\" and \"overall win rate\".
Here's a formula to calculate your return on investment in tournaments:
Tracking tools provide a plethora of statistics, displaying details about various aspects of a player's performance, such as -
The frequency with which a player folds to a continuation bet on each street.
Calculating Tournament Winrate
Indeed, almost any conceivable scenario can be documented. Many poker tracking programs allow users to create customized statistics.
- How often a player fires a continuation bet on each street.
- Serious players invest ample time analyzing their poker statistics, comparing their performances with those of skilled winning players. This technique is excellent for identifying leaks in their game, facilitating a swift review of a large sample of hands.
- How often a player 3bets preflop.
- How often a player folds to a preflop 3bet
- How often a player raises the flop
Numerous poker enthusiasts have firsthand experience working with extensive databases of statistics. They maximize their insights by applying various filters to uncover weaknesses.
Applying Poker Statistics for Database Analysis - Key Statistics
stands for 'voluntarily put in pot,' which represents the percentage of starting hands that we engage with. In 6-max No-Limit Hold'em, a VPIP of 20 to 28% is typically anticipated.
denotes 'preflop raiser' and describes the percentage of starting hands we opt to raise before the flop. A PFR in the range of 16 to 23% would be customarily expected in 6-max No-Limit Hold'em.
- VPIP
VPIP refers to a re-raise during the preflop betting round when confronting an open raise. Often, 3-betting against an open raise can reap more rewards than merely calling. Successful 6-max players usually maintain a 3-bet rate of approximately 7-9% . - PFR
PFR applies when we merely call an open raise preflop. Although opportunities to 3-bet exist, cold-calling remains a fundamental aspect of effective strategy. Regular winning 6-max players typically have a cold-call percentage of around 12% . - Preflop 3bet
A preflop 3bet Discover additional methods to enhance your gameplay here.
- Cold-call
A preflop cold-call 4. Leveraging Poker Statistics for Opponent Analysis
If we can scrutinize our own data, we can undoubtedly analyze our opponents as well.
We can investigate their statistics similarly to how we assess our own, but now we have a different intention.
Our goal is to uncover flaws in our opponent's strategy that we can take advantage of. opponent’s data.
Here is a reference chart outlining the characteristics of opponents we may encounter:
Using-Poker-Villain-Types-as-Statistics
Utilizing Poker Villain Types as Statistics
Poker Statistics - 7 Practical Applications for Analyzing Gameplay
In what ways do statistics play a crucial role in shaping the perspective of a skilled poker player? Overlay Players can leverage poker statistics to modify their approach and enhance their abilities.
This article aims to guide you on how to interpret and utilize poker statistics through several key topics.
Let’s examine 7 effective methods for implementing statistics within the poker landscape.
Analyzing Databases with Poker Statistics
Utilizing Poker Statistics for Opponent Insights
- Fold to Cbet
Fold Employing Poker Statistics for Broader Player Analysis - Fold to 3bet
Poker players estimate the likelihood of a specific hand being successful, basing their calculations on the number of available 'outs' that remain in the deck. - Fold to Steal
Fold when facing an open- raise This scenario will occur about 36% of the time by the river. Such calculations are more aligned with probability than traditional poker statistics.
- Raise vs Flop Cbet
When players try to memorize crucial values in advance, that falls under the umbrella of poker statistics. laydowns when facing flop raises.
Instead of trying to compute values during a hand, seasoned players prefer to commit to memory the pre-calculated figures.
Here’s an example of a set of statistics that a poker player might want to become familiar with. poker-room , limit, or network.
The table below illustrates the probabilities of achieving certain hands based on the number of outs and where the game is at.
Naturally, all these figures can be determined using methods from the field of probability.
However, doing these calculations mid-hand can waste precious time, which is why many players opt to simply memorize these essential statistics.
Key Odds for Hitting a Hand
Achieving a flopped flush draw by the river - 35% game theory correct poker.
on the flop, you can expect to complete your flush around 35% of the time by the river. If only the turn is seen, the likelihood decreases significantly.
It's beneficial to recall the statistics related to completing different types of hands. This approach tends to be more effective than attempting to perform calculations during play.
- Fold to flop float bet.
A float Achieving a flopped open-ended straight draw by the river - 31.5% - Fold to delayed cbet.
This type of straight draw will hit approximately 31.5% of the time at the river, assuming both the turn and river cards are dealt. - Fold to turn probe bet.
A probe Hitting a flopped gutshot by the river - 16.5%
- Fold to stop and go.
The term ‘ stop and go A gutshot straight draw has about a 16.5% chance of completing by the river.
6. Poker Statistics in GTO Play
When entering a hand with pocket pairs before the flop, you can expect to hit a set around 11.8% of the time. This statistic is useful for determining whether chasing sets is a profitable strategy.
Additionally, 'pot odds' and 'break-even points' can also be computed in real-time using probability principles. Many players, however, prefer to memorize these crucial figures. GTO poker strategy The preceding table may be perplexing for individuals lacking a foundation in poker theory .
Required Equity to Call – Also referred to as 'Pot odds'. This differs from the 'odds of hitting' discussed earlier in our statistics applications. ' solver ', when expressed as a percentage, represents the proportion of the total pot we would risk when making a call.
This statistic aligns with the proportion of pot-equity needed to break even when completing the action.
For instance, the chart indicates that if our opponent places a bet equal to 50% of the pot, we would be risking 25% of the total pot if we decided to call.
– This figure represents the required bluffing frequency (at a specific bet size) necessary to win the pot outright (excluding any pot equity consideration).
For example, a bet of 50% of the pot needs to succeed 33.33% of the time for it to be deemed profitable.
These statistics can all be calculated on the fly using probability rules. Yet, most serious players prefer to adopt a statistics-based model by memorizing essential values.
- Game Tree
Pot Odds and Break-Even Values - Key Statistics - Mix Strategy
The table below reveals our pot odds (expressed as percentages) when confronting typical bet sizes: - Range Advantage
When one player’s range to call against a half pot bet on the river - 25%
- Preflop Solve
When facing a half-pot bet, we must have winning chances more than 25% of the time in order to call profitably. It’s advantageous to internalize these basic statistics rather than attempting to calculate them dynamically.
Required equity to call facing a pot-sized bet on the river - 33%
7. General Poker Stats
When up against a pot-sized bet, we need to have a favorable hand over 33% of the time to make the call worthwhile. We should not necessarily be the favorite since there are already chips in play. online poker .
Break-even point on a half pot river bluff - 33%
- 5% of poker players are winning players.
- Less than 1% go on to make big money.
Making a half-pot bluff becomes profitable if our opponent folds more than 33% of the time. It can be advantageous to bet with weaker hands if we suspect significant fold equity.
Break-even point on a pot-sized river bluff - 50%
A pot-sized bluff must succeed more than 50% of the time to yield a profit.
Basic Maths
3. Utilizing Poker Statistics for Database Analysis
Basic Probabilities
Basic probability Players engaged in online poker often monitor their hands using tracking software. This software logs every hand played and aggregates the data to showcase critical stats like 'number of hands played' and 'overall win rate'.
Preflop 3bet
Here is a formula to calculate your return on investment (ROI) during tournaments: A preflop Tracking software provides an extensive array of statistics, including insights into specific aspects of a player's performance, such as -
The frequency with which a player folds to a continuation bet on each street.
3bet
Dedicated players spend an immense amount of time sifting through their poker stats, comparing their results to successful players'. This process is instrumental in identifying leaks , allowing for a swift analysis of a wide sample of hands.
Many poker players are well-acquainted with using a database of statistics. They employ it to investigate weaknesses in their game through a variety of filters .
Cold-call